Can Easy Off Clean Cuisinart 5 In 1 Griddler Greasy Coils
The friction force is the force exerted by a surface when an object moves across information technology - or makes an effort to motion beyond it.
The frictional force can exist expressed as
Ff = μ Due north (1)
where
Ff = frictional force (N, lb)
μ = static (μs) or kinetic (μk) frictional coefficient
N = normal force betwixt the surfaces (N, lb)
At that place are at least ii types of friction forces
- kinetic (sliding) friction force- when an object moves
- static friction force - when an object makes an effort to move
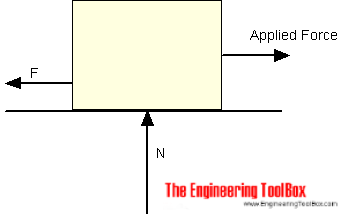
For an object pulled or pushed horizontally the normal force - N - is only the gravity force - or weight:
N = Fg
= m a1000 (2)
where
Fg = gravity force - or weight (N, lb)
grand = mass of object (kg, slugs)
aone thousand = acceleration of gravity (9.81 m/stwo, 32 ft/due south2)
The friction forcefulness due to gravity (1) can with (ii) be modified to
Ff = μ mag (3)
Friction Force Calculator
m - mass (kg, slugs)
am - acceleration og gravity (9.81 g/sii, 32 ft/s2)
μ - friction coefficient
- Friction forces on inclined planes
- Weight vs mass - the difference
Friction Coefficients for some Mutual Materials and Materials Combinations
| Materials and Material Combinations | Surface Conditions | Frictional Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static - μstatic - | Kinetic (sliding) - μsliding - | |||
| Aluminum | Aluminum | Clean and Dry | i.05 - 1.35 | 1.4 |
| Aluminum | Aluminum | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.3 | |
| Aluminum-bronze | Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.45 | |
| Aluminum | Mild Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.61 | 0.47 |
| Aluminum | Snow | Wet 0oC | 0.4 | |
| Aluminum | Snowfall | Dry 0oC | 0.35 | |
| Brake textileii) | Cast iron | Make clean and Dry | 0.iv | |
| Brake fabric2) | Cast atomic number 26 (wet) | Clean and Dry | 0.2 | |
| Brass | Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.51 | 0.44 |
| Brass | Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.19 | |
| Brass | Steel | Castor oil | 0.11 | |
| Brass | Cast Iron | Clean and Dry | 0.3 | |
| Brass | Ice | Clean 0oC | 0.02 | |
| Brass | Ice | Make clean -80oC | 0.15 | |
| Brick | Woods | Clean and Dry | 0.6 | |
| Bronze | Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.16 | |
| Bronze | Cast Iron | Clean and Dry | 0.22 | |
| Bronze - sintered | Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.13 | |
| Cadmium | Cadmium | Clean and Dry | 0.v | |
| Cadmium | Cadmium | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.05 | |
| Cadmium | Chromium | Make clean and Dry out | 0.41 | |
| Cadmium | Chromium | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.34 | |
| Cadmium | Mild Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.46 | |
| Bandage Iron | Cast Iron | Clean and Dry | one.1 | 0.15 |
| Cast Iron | Cast Atomic number 26 | Clean and Dry | 0.15 | |
| Bandage Iron | Bandage Iron | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.07 | |
| Cast Iron | Oak | Clean and Dry out | 0.49 | |
| Bandage Iron | Oak | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.075 | |
| Cast iron | Mild Steel | Clean and Dry out | 0.4 | |
| Cast atomic number 26 | Mild Steel | Clean and Dry out | 0.23 | |
| Cast iron | Mild Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.21 | 0.133 |
| Car tire | Asphalt | Make clean and Dry out | 0.72 | |
| Car tire | Grass | Clean and Dry | 0.35 | |
| Carbon (hard) | Carbon | Make clean and Dry | 0.16 | |
| Carbon (hard) | Carbon | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.12 - 0.xiv | |
| Carbon | Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.xiv | |
| Carbon | Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.eleven - 0.14 | |
| Chromium | Chromium | Make clean and Dry out | 0.41 | |
| Chromium | Chromium | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.34 | |
| Copper-Atomic number 82 alloy | Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.22 | |
| Copper | Copper | Clean and Dry | 1.6 | |
| Copper | Copper | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.08 | |
| Copper | Cast Iron | Make clean and Dry | 1.05 | 0.29 |
| Copper | Mild Steel | Clean and Dry out | 0.53 | 0.36 |
| Copper | Balmy Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.xviii | |
| Copper | Mild Steel | Oleic acid | 0.18 | |
| Copper | Glass | Clean and Dry | 0.68 | 0.53 |
| Cotton | Cotton | Threads | 0.iii | |
| Diamond | Diamond | Make clean and Dry | 0.one | |
| Diamond | Diamond | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.05 - 0.one | |
| Diamond | Metals | Clean and Dry | 0.1 - 0.xv | |
| Diamond | Metal | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.1 | |
| Garnet | Steel | Clean and Dry out | 0.39 | |
| Glass | Drinking glass | Clean and Dry | 0.9 - 1.0 | 0.4 |
| Drinking glass | Glass | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.one - 0.6 | 0.09 - 0.12 |
| Glass | Metal | Make clean and Dry out | 0.5 - 0.7 | |
| Glass | Metallic | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.2 - 0.3 | |
| Glass | Nickel | Clean and Dry | 0.78 | |
| Glass | Nickel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.56 | |
| Graphite | Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.1 | |
| Graphite | Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.i | |
| Graphite | Graphite (in vacuum) | Clean and Dry | 0.5 - 0.eight | |
| Graphite | Graphite | Clean and Dry out | 0.1 | |
| Graphite | Graphite | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.1 | |
| Hemp rope | Timber | Make clean and Dry | 0.5 | |
| Horseshoe | Prophylactic | Clean and Dry | 0.68 | |
| Horseshoe | Concrete | Clean and Dry | 0.58 | |
| Ice | Water ice | Make clean 0oC | 0.i | 0.02 |
| Ice | Ice | Clean -12oC | 0.3 | 0.035 |
| Water ice | Water ice | Make clean -80oC | 0.five | 0.09 |
| Water ice | Wood | Clean and Dry out | 0.05 | |
| Ice | Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.03 | |
| Fe | Iron | Make clean and Dry | 1.0 | |
| Iron | Iron | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.15 - 0.20 | |
| Lead | Cast Iron | Clean and Dry | 0.43 | |
| Leather | Oak | Parallel to grain | 0.61 | 0.52 |
| Leather | Metallic | Make clean and Dry | 0.4 | |
| Leather | Metallic | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.2 | |
| Leather | Wood | Clean and Dry | 0.3 - 0.iv | |
| Leather | Clean Metal | Clean and Dry | 0.6 | |
| Leather | Cast Iron | Clean and Dry | 0.6 | 0.56 |
| Leather cobweb | Cast fe | Clean and Dry | 0.31 | |
| Leather fiber | Aluminum | Clean and Dry | 0.xxx | |
| Magnesium | Magnesium | Clean and Dry | 0.6 | |
| Magnesium | Magnesium | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.08 | |
| Magnesium | Steel | Make clean and Dry out | 0.42 | |
| Magnesium | Cast Iron | Clean and Dry | 0.25 | |
| Masonry | Brick | Clean and Dry out | 0.6 - 0.7 | |
| Mica | Mica | Freshly broken | 1.0 | |
| Nickel | Nickel | Clean and Dry | 0.seven - 1.ane | 0.53 |
| Nickel | Nickel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.28 | 0.12 |
| Nickel | Balmy Steel | Make clean and Dry | 0.64 | |
| Nickel | Mild Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.178 | |
| Nylon | Nylon | Make clean and Dry | 0.xv - 0.25 | |
| Nylon | Steel | Clean and Dry out | 0.4 | |
| Nylon | Snow | Wet 0oC | 0.four | |
| Nylon | Snow | Dry -xoC | 0.iii | |
| Oak | Oak (parallel grain) | Clean and Dry | 0.62 | 0.48 |
| Oak | Oak (cross grain) | Clean and Dry out | 0.54 | 0.32 |
| Oak | Oak (cross grain) | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.072 | |
| Paper | Cast Iron | Clean and Dry out | 0.20 | |
| Phosphor-statuary | Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.35 | |
| Platinum | Platinum | Make clean and Dry | 1.two | |
| Platinum | Platinum | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.25 | |
| Plexiglas | Plexiglas | Clean and Dry | 0.8 | |
| Plexiglas | Plexiglas | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.eight | |
| Plexiglas | Steel | Clean and Dry out | 0.four - 0.5 | |
| Plexiglas | Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.iv - 0.five | |
| Polystyrene | Polystyrene | Clean and Dry | 0.5 | |
| Polystyrene | Polystyrene | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.5 | |
| Polystyrene | Steel | Clean and Dry out | 0.3 - 0.35 | |
| Polystyrene | Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.3 - 0.35 | |
| Polyethylene | Polytehylene | Make clean and Dry | 0.two | |
| Polyethylene | Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.2 | |
| Polyethylene | Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.2 | |
| Rubber | Rubber | Clean and Dry | one.16 | |
| Condom | Cardboard | Clean and Dry | 0.5 - 0.eight | |
| Prophylactic | Dry Cobblestone | Clean and Dry out | 0.nine | 0.5 - 0.8 |
| Rubber | Wet Asphalt | Make clean and Dry | 0.25 - 0.75 | |
| Rubber | Dry Physical | Make clean and Dry | 0.vi - 0.85 | |
| Rubber | Wet Concrete | Make clean and Dry out | 0.45 - 0.75 | |
| Silk | Silk | Clean | 0.25 | |
| Silverish | Silver | Clean and Dry | 1.4 | |
| Silver | Silver | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.55 | |
| Sapphire | Sapphire | Clean and Dry | 0.two | |
| Sapphire | Sapphire | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.2 | |
| Silver | Silver | Clean and Dry | one.4 | |
| Silver | Silverish | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.55 | |
| Skin | Metals | Clean and Dry | 0.8 - 1.0 | |
| Steel | Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.5 - 0.8 | 0.42 |
| Steel | Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.16 | |
| Steel | Steel | Castor oil | 0.fifteen | 0.081 |
| Steel | Steel | Stearic Acrid | 0.15 | |
| Steel | Steel | Light mineral oil | 0.23 | |
| Steel | Steel | Lard | 0.11 | 0.084 |
| Steel | Steel | Graphite | 0.058 | |
| Steel | Graphite | Clean and Dry | 0.21 | |
| Straw Fiber | Cast Iron | Clean and Dry | 0.26 | |
| Straw Fiber | Aluminum | Make clean and Dry out | 0.27 | |
| Tarred cobweb | Cast Atomic number 26 | Clean and Dry | 0.fifteen | |
| Tarred fiber | Aluminum | Clean and Dry | 0.18 | |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) (Teflon) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Clean and Dry out | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.04 | |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.05 - 0.two | |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Snow | Wet 0oC | 0.05 | |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | Snow | Dry out 0oC | 0.02 | |
| Tungsten Carbide | Steel | Clean and Dry | 0.4 - 0.6 | |
| Tungsten Carbide | Steel | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.1 - 0.2 | |
| Tungsten Carbide | Tungsten Carbide | Make clean and Dry | 0.2 - 0.25 | |
| Tungsten Carbide | Tungsten Carbide | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.12 | |
| Tungsten Carbide | Copper | Clean and Dry out | 0.35 | |
| Tungsten Carbide | Iron | Clean and Dry | 0.8 | |
| Tin | Cast Iron | Make clean and Dry | 0.32 | |
| Tire, dry | Road, dry | Clean and Dry | 1 | |
| Tire, wet | Road, wet | Clean and Dry out | 0.two | |
| Wax, ski | Snow | Moisture 0oC | 0.one | |
| Wax, ski | Snow | Dry 0oC | 0.04 | |
| Wax, ski | Snow | Dry out -10oC | 0.2 | |
| Woods | Clean Forest | Clean and Dry | 0.25 - 0.5 | |
| Wood | Wet Woods | Make clean and Dry | 0.ii | |
| Forest | Clean Metal | Clean and Dry | 0.ii - 0.six | |
| Wood | Moisture Metals | Clean and Dry | 0.2 | |
| Wood | Stone | Make clean and Dry | 0.2 - 0.4 | |
| Forest | Physical | Clean and Dry | 0.62 | |
| Forest | Brick | Clean and Dry | 0.6 | |
| Wood - waxed | Wet snow | Clean and Dry out | 0.14 | 0.one |
| Forest - waxed | Dry snow | Clean and Dry | 0.04 | |
| Zinc | Cast Iron | Make clean and Dry | 0.85 | 0.21 |
| Zinc | Zinc | Make clean and Dry | 0.half dozen | |
| Zinc | Zinc | Lubricated and Greasy | 0.04 | |
Kinetic or sliding frictional coefficient only when there is a relative motion between the surfaces.
Note! It is unremarkably thought that the static coefficients of friction are higher than the dynamic or kinetic values. This is a very simplistic statement and quite misleading for brake materials. With many restriction materials the dynamic coefficient of friction quoted is an "average" value when the material is subject to a range of sliding speeds, surface pressures and most importantly operating temperatures. If the static situation is considered at the aforementioned pressure level, only at ambient temperature, then the static coefficient of friction is oftentimes significantly LOWER than the average quoted dynamic value. Information technology can be every bit low as 40 - fifty% of the quoted dynamic value.
Kinetic (Sliding) versus Static Frictional Coefficients
Kinetic or sliding frictional coefficients are used with relative move betwixt objects. Static frictional coefficients are used for objects without relative motion. Note that static coefficients are somewhat higher than the kinetic or sliding coefficients. More forcefulness are required to start a move
Example - Friction Force
A 100 lb wooden crate is pushed across a concrete floor. The friction coefficient betwixt the object and the surface is 0.62. The friction strength can be calculated as
Ff = 0.62 (100 lb)
= 62 (lb)
- 1 lb = 0.4536 kg
Example - Car, Braking, Friction Force and Required Distance to Stop

A automobile with mass 2000 kg drives with speed 100 km/h on a wet road with friction coefficient 0.2.
Note! - The friction work required to end the car is equal to the kinetic free energy of the auto.
The kinetic energy of the car is
Eastkinetic = 1/2 g v2 (iv)
where
Ekinetic = kinetic energy of the moving car (J)
m = mass (kg)
v = velocity (one thousand/southward)
Ekinetic = 1/two (2000 kg) ((100 km/h) (one thousand m/km) / (3600 due south/h))2
= 771605 J
The friction work (free energy) to finish the car can be expressed as
Wfriction = Ff d (5)
where
Wfriction = friction work to stop the automobile (J)
Ff = friction force (Due north)
d = braking (stopping) altitude (k)
Since the kinetic free energy of the car is converted to friction energy (piece of work) - we have the expression
Ekinetic = Due westfriction (6)
The friction force Ff can be calculated from (three)
Ff = μ m g
= 0.two (2000 kg) (9.81 m/s2)
= 3924 Northward
The stop altitude for the automobile can be calculated by modifying (five) to
d = Wfriction / Ff
= (771605 J) / (3924 N)
= 197 yard
Note! - since the mass of the motorcar is nowadays on both sides of eq. 6 it cancels out. The finish distance is non dependent on the mass of the machine.
"Laws of Friction"
Unlubricated Dry out Surfaces
- for low pressure the friction is proportional to the normal strength betwixt the surfaces. With rising pressure the friction will not ascent proportionally. With extreme pressure friction will rise and surfaces seize.
- at moderate force per unit area the friction force - and coefficient - is not dependent of the surface areas in contact as long every bit the normal force is the aforementioned. With farthermost pressure friction will rice and surfaces seize.
- at very low velocity between the surfaces the friction is independent of the velocity of rubbing. With increased velocity the the friction decrease.
Lubricated Surfaces
- friction strength is almost independent of force per unit area - normal strength - if the surfaces are flooded with lubricant
- friction varies with speed at depression force per unit area. At college pressure the minimum friction is at velocity ii ft/s (0.7 m/southward) and friction increases with approximately square root of velocity subsequently.
- friction varies with temperature
- for well lubricated surfaces the friction is almost independent of surface textile
Typically steel on steel dry static friction coefficient 0.8 drops to 0.iv when sliding is initiated - and steel on steel lubricated static friction coefficient 0.16 drops to 0.04 when sliding is initiated.
Source: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/friction-coefficients-d_778.html
Posted by: hughtitheivelt.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Can Easy Off Clean Cuisinart 5 In 1 Griddler Greasy Coils"
Post a Comment